
Agile for AI: How to Select the Right Framework
Authored by:
-Ahmed Dereaa, Agile Coach | Agile Business Consultant at Vidsccola DAC | Working on Agile Transformation for Al Products
Co-authored by:
-Ahmed Osama – Head of Data Analytics and Al
-Mohamed Salah – Senior Scrum Master
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence and Data Science have become critical drivers for business success, raising an essential question: do traditional Agile frameworks effectively support these teams? While Agile originated in software development, its underlying values of adaptability, collaboration, and rapid feedback provide significant benefits when carefully tailored to the unique lifecycle of AI and data-driven products. However, using Scrum in AI contexts can be particularly challenging due to extensive data exploration, inherent ambiguity, lengthy experimentation cycles, and unpredictable outcomes. This guide introduces a practical approach to aligning Agile methodologies with the specific demands of the three distinct phases of AI product development: Discovery, Implementation, and Deployment.
Agile is a Mindset, not a One-Size-Fits-All Framework
Agile isn’t about sticking blindly to Scrum ceremonies or Kanban boards. It’s a mindset rooted in adaptability, collaboration, and continuous learning—perfectly suited for AI teams working in ambiguous and fast-evolving problem spaces. By aligning Agile values with the structure of the data science lifecycle, teams can gain clarity, speed, and sustainability.
Visualizing the Agile Lifecycle for AI Teams
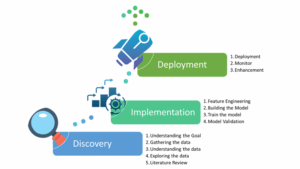
Phase 1: Discovery
The Thinking Phase — Where AI Begins with Questions, Not Code
This phase lays the groundwork for the product. The team explores the business problem, understands available data, and forms initial hypotheses.
Team Roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, Data Scientist, Data Engineer
Inputs: Business goals, data sources
Processes:
-Goal clarification
-Data acquisition and profiling
-Exploratory data analysis
-Literature review
Outputs:
-Product Vision and Roadmap
–Product Backlog Items (Releases, Epics, and User Stories)
Progress Measurement:
–Cycle time for backlog item creation
–Team velocity (in terms of story creation and refinement)
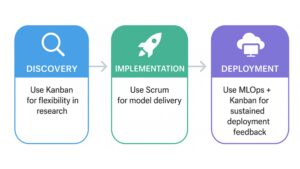
Framework Tip: Kanban works well in this phase to allow flow-based, research-heavy tasks to proceed without artificial sprint pressure.
Phase 2: Implementation
From Hypothesis to Code — Turning Ideas into Working Models
This is the most iterative and technically intensive phase. The focus is on transforming backlog items into machine learning models through a continuous loop of experimentation and refinement.
Team Roles: Data Scientists, Data Engineers, Scrum Master, Product Owner
Inputs: Refined Product Backlog from Phase 1
Processes:
-Feature engineering
-Model building
-Model training
-Validation and evaluation
Outputs:
-Model artifacts
-Performance metrics
-Updated backlog items
Progress Measurement:
-New team velocity calibrated for model development
-Cycle time per iteration or experiment
-Sprint burndown charts
Framework Tip: Scrum fits naturally here, with short sprints enabling rapid feedback, technical reviews, and incremental delivery.
Phase 3: Deployment & Monitoring
From Code to Impact — Operationalizing Models Responsibly
Deployment is where models become products. But the real work begins after go-live: monitoring, detecting drift, and retraining models to keep them reliable and valuable.
Team Roles: MLOps Engineers, Developers, Product Owner
Inputs: Production-ready models and baseline metrics
Processes:
-Model deployment via CI/CD
-Performance monitoring
-Drift detection (data, concept, model)
-Retraining triggers
Outputs:
-Live models in production
-Monitoring dashboards
-Retraining and issue resolution tasks
Progress Measurement:
-Time to deploy (Cycle time)
-Uptime & latency
-Model performance over time
-Incident resolution time
Framework Tip: A DevOps-infused Kanban ensures continuous feedback, high alignment, and rapid adaptation.
Diagram to Conclude
![]()
Final Thoughts: Don’t Force Fit, Tailor Instead
Agile in AI isn’t about finding the perfect framework—it’s about designing a way of working that evolves with your data product. Teams should embrace experimentation not only in models, but also in their Agile practices.
Adapt your framework to the phase, your mindset to the mission, and your velocity to the value.
Learn more: http://www.vidscola.com
Enterprise Agile Services: https://vidscola.com/coaching/